Get a Natural Boost With These Caffeine-Free Energy Drinks
An energy drink can get you through a mid-afternoon slump and deliver the oomph you need pre-workout. The problem is, many energy drinks pack high levels of caffeine. (Cue jitters, GI issues, headaches, and insomnia.)
Before you go defending your beloved Celsius, caffeine isn’t necessarily bad for you. It’s a natural stimulant that has many health benefits. A review in Nutrition Bulletin reveals that it can boost mood and alertness at 37.5 milligrams (mg) per day—that’s less than the caffeine you’d find in a cup of coffee (1, 2). But if you drink the equivalent of 4 cups of caffeinated coffee daily, those benefits could give way to side effects (3). Some people’s caffeine tolerance is so low that it doesn’t take much to feel restless and have trouble sleeping, and some find that even small amounts heighten feelings of anxiety.
What do you do when you need a boost, but don’t want a highly caffeinated energy drink or another cup of coffee? Caffeine-free energy drinks could be the answer. Caffeine-free energy drinks rely on other ingredients to perk you up. Popular choices include amino acids, B vitamins, and electrolytes. Each ingredient works differently, but they have one thing in common: They provide energy without the jitters.
So, if you’re searching for a caffeine-free pick-me-up, look no further. We rounded up five caffeine-free, sugar-free options to try.
The 5 Best Caffeine-Free Energy Drinks
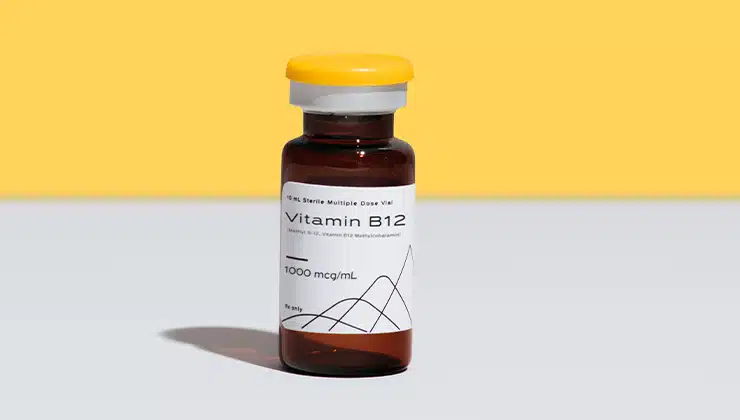
Vitamin B12, now available from Hone, may boost your energy, reduce stress, and support your brain. Connect with a doctor to see if it’s right for you.
References
1. Ruxton, CHS. (2008). The impact of caffeine on mood, cognitive function, performance and hydration: A review of benefits and risks
2. Information about caffeine in coffee. USDA FoodData Central.
3. Mayo Clinic. (2022). Caffeine: How much is too much?
4. B vitamins. MedlinePlus.
5. Viribay A, et al. (2020). Effects of arginine supplementation on athletic performance based on energy metabolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis
6. Tyrosine. Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
7. Epinephrine (Adrenaline). Cleveland Clinic.
8. Tumilty L, et al. (2011). Oral tyrosine supplementation improves exercise capacity in the heat