This Bodybuilder Eats 100 Egg Whites a Day. But What About the Yolks?
Fast Facts
- Eggs are a high-quality source of protein.
- Egg whites are high in protein and lower in saturated fat and calories than whole eggs.
- Egg yolks are loaded with vitamins and minerals that can boost workout recovery and keep you satiated.
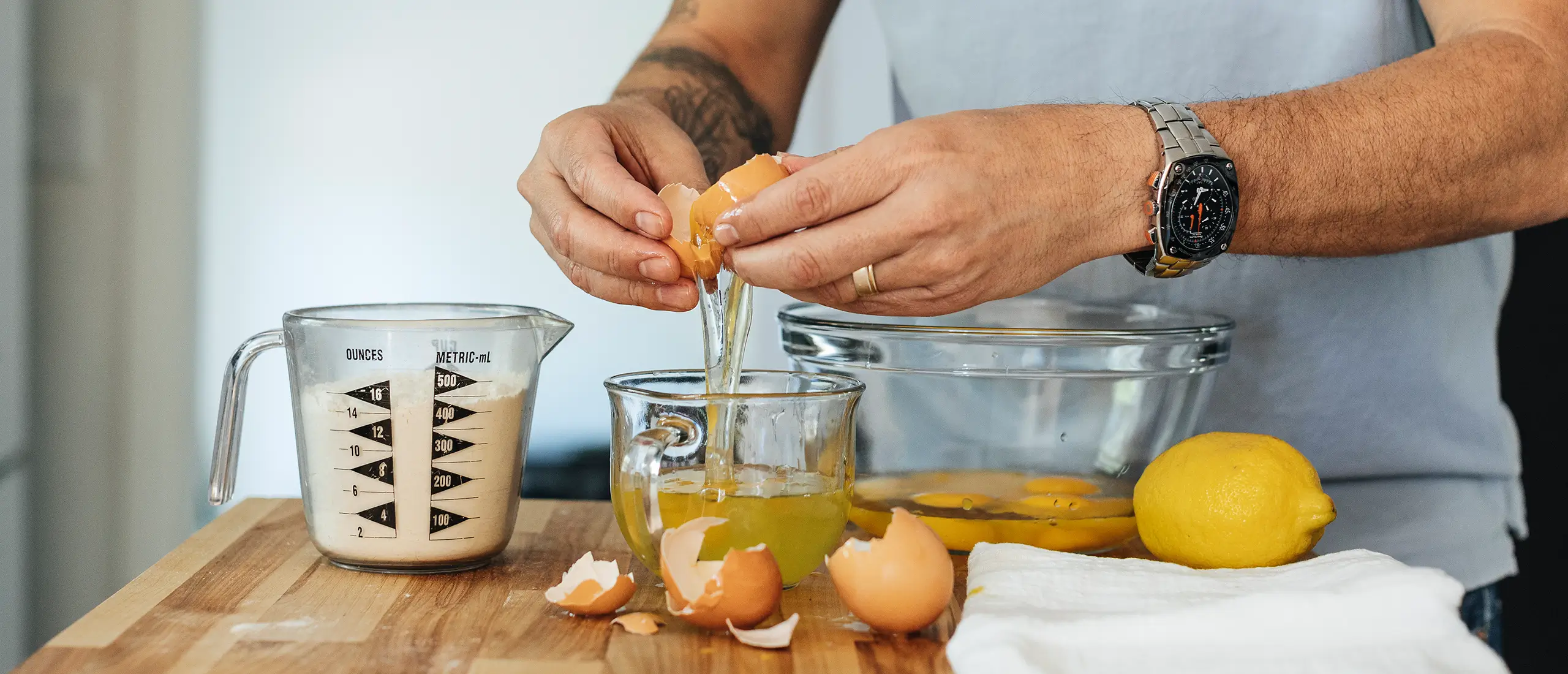
In a recent TikTok post, Fernando Torraca aka “The King of Diet” shared a video of him cracking several cartons of eggs, separating them into yolks and whites, and pouring the yolks down the drain.
This isn’t the first time the bodybuilder has shared about his egg-heavy diet. In July, Toracca posted a YouTube video explaining why he eats a whopping 100 eggs a day. “I don’t eat the whole eggs…only the egg whites,” he says.
But should you ditch the egg yolks like Torraca? And how many should you eat for benefits? We dig into the nutrition below.
Eggs vs. Egg Whites
Eggs are a very convenient source of protein, which is why many fitness enthusiasts turn to them to fulfill their daily needs. If your goal is to build muscle, both egg whites, and whole eggs will get the job done.
But eggs and egg whites aren’t equal. Here’s how they stack up.
Egg Whites
Egg whites are an excellent source of high-quality protein, containing all the essential amino acids your body needs. They’re also lower in calories and saturated fat than a whole egg which makes them an ideal lean protein source if you’re looking to lose weight.
But egg whites don’t offer much more than protein. By leaning on egg whites for protein are missing out on all of the nutrition packed in the egg yolk.
Whole Eggs
Most people looking to build fitness and maintain health will be better served eating the whole egg. They might be higher in calories, but the majority of nutrients are found in the yolk.
Egg yolks contain high amounts of choline, selenium, and vitamins A, D, E, and K. They’re also rich in vitamin B12, which plays an important role in fat and protein metabolism, and can boost your energy and mood.
Plus, when it comes to muscle recovery, the whole egg seems to have an edge. A recent review found that eating a whole egg promotes greater acute muscle protein synthesis in comparison to egg whites (1).
Whole eggs have also gotten a bad rap for their high cholesterol content. But according to a recent study, much of the cholesterol in eggs actually synthesizes into vitamin D and hormones, including testosterone, an anabolic hormone that plays an essential role in the maintenance of muscle mass and strength (2).
A recent study found that eating three whole eggs increased testosterone levels in comparison to six egg whites, but the increase was not enough to enhance gains in muscle mass (3).
These findings show more studies are needed to evaluate the effects the amount of whole eggs you eat can have on testosterone levels.
How Many Eggs to Eat in a Day?
For most people, 100 eggs a day is excessive. Not to mention, a lot for your body to process in one sitting.
If you want to look like The King of Diet or The Rock, what it really boils down to is eating a healthy diet that includes adequate protein to meet your energy needs.
The amount of protein you should eat depends on your weight and training schedule. To increase muscle mass, the American College of Sports Medicine recommends 1.2 or 1.7 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight.
On the high end, that’s about 155 grams of protein per day for a 200-pound man. If eating four meals per day that amounts to about 39 grams of protein per meal, or about six eggs.
But just because you can get all your protein needs from eggs, doesn’t mean you should. A healthy diet includes a diverse variety of foods that are rich in different vitamins, minerals, and nutrients. Aim to add eggs into the mix, rather than depend on them for all your protein needs.
Bottomline
Gram for gram, eggs are one of the highest-quality sources of protein available. If you simply prefer the taste of egg whites or have specific weight loss goals, there’s no harm in enjoying them. Otherwise, you’re much better off eating the whole egg, as the yolks are packed with essential vitamins and minerals.
References
1. Santos, H. et al (2021). The Effect of Whole Egg Intake on Muscle Mass: Are the Yolk and Its Nutrients Important? https://journals.humankinetics.com/view/journals/ijsnem/31/6/article-p514.xml
2. Huff, T. et al (2022). Physiology, Cholesterol. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470561/
3. Reza, B. et al (2021). Whole Egg Vs. Egg White Ingestion During 12 Weeks of Resistance Training in Trained Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. https://journals.lww.com/nsca-jscr/Abstract/2021/02000/Whole_Egg_Vs__Egg_White_Ingestion_During_12_weeks.17.aspx