The Absolute Worst Foods for Erectile Dysfunction
- By Rebekah Harding
- Fact-checked by Joy Ferguson
- July 24, 2023
A fancy, steak dinner followed by a few drinks seems like a great primer for a steamy night-in. But your order could actually kill your erection before you even make it to the bedroom. That’s because alcohol and meats high in saturated fat are among the worst foods for erectile dysfunction.
What Causes Erectile Dysfunction?
Getting an erection isn’t as simple as it seems. In order to get and maintain an erection, your hormones, blood vessels, mental health, and nerves all need to cooperate. Even if just one element is out of whack, you may start to have trouble staying hard.
It’s estimated that more than 30 million men in the United States have erectile dysfunction, or ED—the persistent inability to get and maintain an erection firm enough for sex—according to the Endocrine Society. ED can be caused by a combination of physical ailments and psychological factors, like cardiovascular disease or performance anxiety.
Around 26 percent of men aged 40 or under had ED, in a study in the Journal of Sexual Medicine (1). Once you hit 50, you are up to 67 percent likely to develop erectile dysfunction, according to some research (2). The increased erectile dysfunction risk with age may be due to conditions like low testosterone, diabetes, and high blood pressure (3).
Certain prescription drugs, including some antidepressants and blood pressure medications, may also cause erectile dysfunction.
Can Your Diet Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Any number of lifestyle factors, like smoking, drug use, and exercise habits can impact erectile function (4).
A poor diet packs a double threat to your manhood.
“While cardiovascular disease and diabetes are the most common causes of erectile dysfunction, poor nutrition is a risk factor for both of these chronic conditions,” says board-certified urologist Amy Pearlman, M.D. “Even in the absence of known chronic disease, a poor diet can also be a primary risk factor for erectile dysfunction.”
A 2020 study of over 20,000 men who had previously participated in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study found that those who stuck to a diet high in vegetables, fruits, nuts, legumes, and fish had a lower risk for erectile dysfunction (5). Many men with low erectile dysfunction risk also avoided red and processed meats.
What’s the connection?
When you’re aroused, nitric oxide (the chemical that helps your blood vessels relax and expand) is released. Nitric oxide causes the blood vessels in your penis to widen so blood can fill it, Pearlman explains. “Inflammation, which can result from eating certain foods, can speed up the destruction of nitric oxide and may contribute to issues with erectile function.”
Worst Foods for Erectile Dysfunction
High Sodium Foods and Processed Foods
Sodium stunts blood flow and raises blood pressure
Your face and stomach might swell after indulging in high-sodium foods like chips and microwave meals, but these eats have the opposite effect on your penis. When you indulge in salty foods, sodium pulls water into your blood vessels (6). This increases the volume of blood in the vessels, which can cause your blood pressure to spike.
You may notice the effects of increased blood pressure—like fatigue, irregular heartbeat, and anxiety—immediately after a salty meal. Over time, high blood pressure can cause the blood vessels to permanently stretch. This can lead to artery-clogging plaque that blocks blood flow, including to your penis. Any factor that stifles blood flow can increase your odds of experiencing erectile dysfunction.
High-salt diets may decrease blood flow to the penis shaft, at least according to a study on rats (7). Researchers found that rats given a high-sodium diet had increased inflammation, blood pressure, and oxidative stress—all factors which may cause sexual dysfunction. When your body is under oxidative stress, you don’t have enough antioxidants to get rid of the unstable molecules in your body. This can lead to cell and tissue damage. While human trials are needed, scientists believe that this suggests that a low sodium diet may support healthy erections.
The worst high-sodium foods
These are the most frequently consumed high-sodium foods by adults, according to the CDC:
- Breads and rolls
- Pizza
- Sandwiches
- Cold cuts and cured meats
- Soups
- Burritos and tacos
- Savory snacks*
- Chicken
- Cheese
- Eggs and omelets
Processed foods cause inflammation
It’s tempting to throw together a quick ham and salami on rye for lunch, but processed meats might keep your penis from optimal performance after work.
Processed meat (hot dogs, bacon, deli meat) may increase inflammation and oxidative stress, according to a 2017 study (8).
Both inflammation and oxidative stress may cause erectile dysfunction due to damage to the thin layer of cells that line your blood vessels that play a key role in immune system regulation and inflammation (9, 10). This can occur when your blood vessels don’t get enough nitric oxide. If your blood vessels aren’t functioning optimally, you may have trouble getting hard.
Trans Fats and Saturated Fats
High cholesterol increases erectile dysfunction risk
The easiest way to spike your bad (LDL) cholesterol levels? Indulge in foods high in trans and saturated fats like fried foods. Trans and saturated fats damage your blood vessels by increasing your cholesterol, according to the American Heart Association.
You have two main types of cholesterol: LDL and HDL. LDL cholesterol—often referred to as the bad kind—makes up the bulk of your body’s cholesterol and is associated with heart disease and stroke. Healthy LDL levels are at or under 100 mg/dL for most adults, according to the American Heart Association. HDL cholesterol—the good kind—should stay above 60 mg/dL.
High levels of LDL cholesterol are linked with poor erectile function, because it increases the risk of other conditions, like heart disease, that lead to erectile dysfunction (11).
Fried foods cause obesity
You’ll want to minimize trips to the drive-thru if you’re concerned about erectile dysfunction.
Obesity is a major risk factor for erectile dysfunction (12). Obese men had three times more risk of developing sexual dysfunction than the general public, and 79 percent of men with erectile dysfunction had BMIs of 25 kg/m2 or more, according to a 2019 study.
Here’s why: obesity is associated with a chronic low-grade inflammatory state and increased oxidative stress, according to the study’s authors. Which, as we’ve mentioned above, is no friend of erections.
The worst high-fat foods
These are the most frequently consumed high-fat foods, according to the CDC:
- Cheese
- Fatty meats
- Dairy-based desserts
- Tropical oils (palm oil)
Excessive Sugar
Sugar impacts insulin resistance
Regularly overdoing the sweet stuff can cause your blood sugar levels to stay permanently elevated, which can raise your insulin resistance and impact your ability to get an erection.
One reason: When your blood sugar levels are consistently high, your pituitary gland has a hard time making adequate luteinizing hormone (LH)—the hormone that sends a signal to your testicles to start making testosterone (13). When your LH levels are low, you may not produce enough testosterone. Erectile dysfunction is a common symptom of low testosterone, which is linked to other conditions like heart disease, diabetes and obesity (14, 15).
High blood sugar, often associated with type 2 diabetes, can damage blood vessels and nerves if left untreated.
Diabetes raises your risk of erectile dysfunction
Studies suggest that up to seventy-five percent of men with diabetes have some degree of erectile dysfunction, compared to 26 percent of men without diabetes (16). Worse, the onset of erectile dysfunction may appear 10 to 15 years sooner than their non-diabetic peers.
Remember: Blood vessel damage from type 2 diabetes is irreversible and can make it difficult to maintain an erection (17).
Men with diabetes often have less norepinephrine- and acetylcholine-positive fibers within the corpus cavernosa—two sections of erectile tissue in the penis shaft that fill with blood to help you get an erection. This can make it difficult for the nervous system to trigger muscle relaxation, which you need to get hard (18).
The worst high-sugar foods
These are some of the common high-sugar culprits, according to the CDC:
- Sweetened coffee and tea
- Candy
- Soft drinks
- Breakfast cereals
- Snack bars
- Energy drinks
Alcohol
Drinking disrupts circulation
Whoever suggested sharing a drink to loosen up before taking things to the bedroom was frankly, wrong. Drinking alcohol, even occasionally, may damper erectile function.
As you know, alcohol makes you relaxed. That’s because it impairs your central nervous system, which can slow blood flow to all areas of your body—including your penis (19).
Alcohol also can cause dehydration, which directly disrupts your circulation, according to the Cleveland Clinic. Having enough blood coursing through your veins is critical to maintain an erection.
Intoxication slows brain signals
‘Whiskey dick’ is definitely real. Getting tipsy can minimize sensation to your penis and slow signals and sensations between your big head and your little head, which can make it difficult for you to stay hard in the moment.
Excessive drinking is also associated with a greater risk for mental health conditions like depression (20), which can cause psychological ED (21, 22).
Alcohol doesn’t play well with ED meds
If you think you can just pop a Viagra before a drunk night out, you’re dead wrong. Literally, in rare cases (23). Mixing Viagra and alcohol can heighten the side effects of the medication, which can cause severe headaches and nausea.
Luckily, tons of brands are jumping on the bandwagon to create booze-y tasting beverages without alcohol.
DRINK ZERO-PROOF
Best Foods for Erectile Function
To keep your member in fighting form, Pearlman suggests eating more fruits, vegetables, nuts, oily fish, and whole grains. These foods can dramatically decrease inflammation (which has been linked to ED) and promote overall improved health.
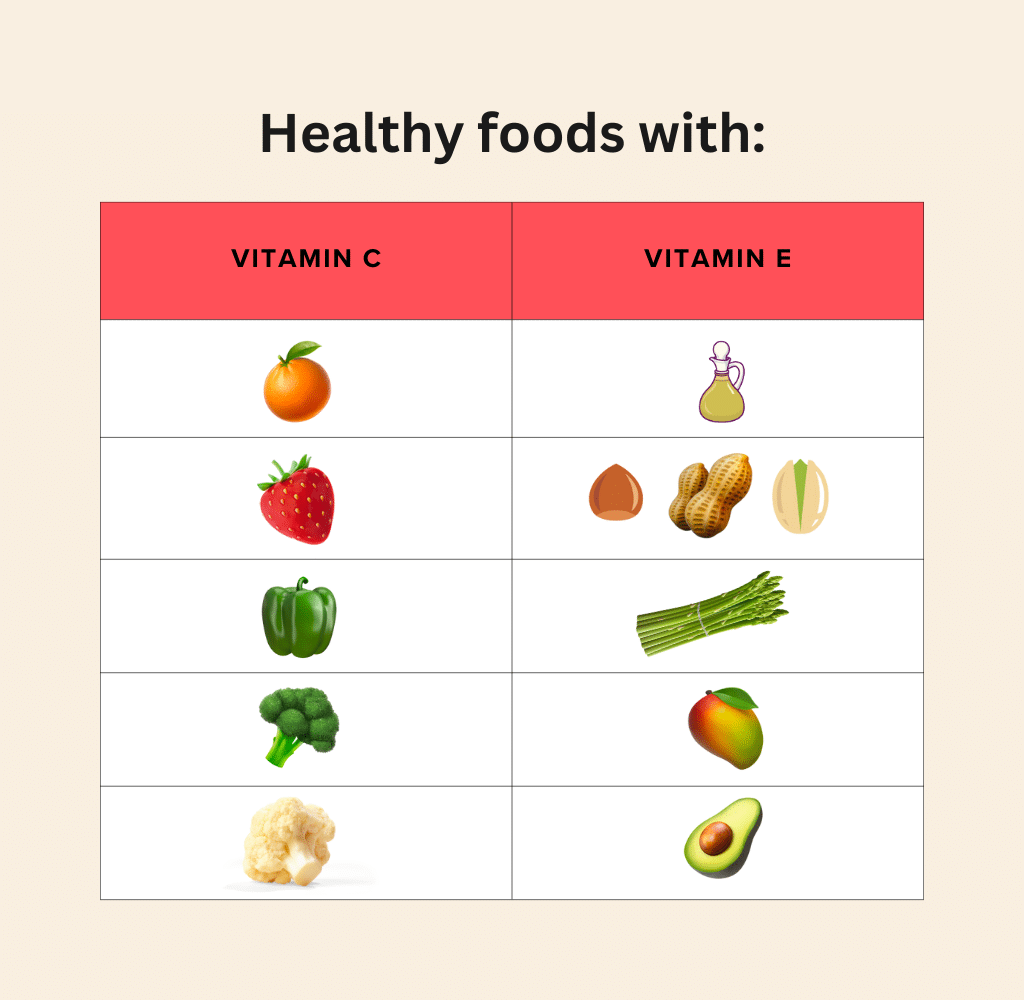
“Foods high in antioxidants, such as Vitamins C and E, have been shown to improve erectile function by preventing damage to cells that produce nitric oxide,” Pearlman says. Here are her recommendations for your next trip to the grocery store:
Healthy foods with Vitamin C:
- Oranges
- Strawberries
- Bell peppers
- Broccoli
- Cauliflower
Healthy foods with Vitamin E:
- Plant-based oils
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Asparagus
- Mango
- Avocado
Other Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction
If you’ve cut out the foods that might be working against your erection, it could be time
to seek medical treatment for your erectile dysfunction.
Pearlman treats men with erectile dysfunction with either stand-alone or tandem treatments that include: focused shockwave therapy, oral phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors, vacuum erection devices, penile constriction bands, intraurethral medication, penile injections, and penile implant surgery.
If you are struggling with erections that aren’t as firm as you’d like or that don’t last long enough,, you should also ask your doctor to test your testosterone levels since ED can be a symptom of low T.
If you want to skip the wait, Hone’s at-home assessment can tell you if your T levels are in a normal range. If results show that your T level is low and ED is one of your symptoms, one of Hone’s partner physicians can help you figure out the best treatment plan. This may include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) and PDE5 inhibitors like sildenafil, vardenafil, tadalafil, or avanafil.
Hone’s test, which you can take from the privacy of your home, can analyze your testosterone levels.
References
1. Capogrosso, et al (2013). One Patient Out of Four with Newly Diagnosed Erectile Dysfunction Is a Young Man—Worrisome Picture from the Everyday Clinical Practice.
2. Shiri, et al (2003). Prevalence and severity of erectile dysfunction in 50 to 75-year-old Finnish men.
3. Ferrini, et al (2017). Aging related erectile dysfunction—potential mechanism to halt or delay its onset.
4. Wu, et al (2012). The association of smoking and erectile dysfunction: results from the Fangchenggang Area Male Health and Examination Survey (FAMHES).
5. Bauer, et al (2020). Association of Diet With Erectile Dysfunction Among Men in the Health Professionals Follow-up Study.
6. Bigler (2020). Pass the Salt: Sodium’s Role in Nerve Signaling and Stress on Blood Vessels.
7. Kishimoto, et al (2020). High Salt Intake Impairs Erectile Function in Salt-Sensitive Rats Through Mineralocorticoid Receptor Pathway Beyond Its Effect on Blood Pressure.
8. Chai, et al (2017). Dietary Red and Processed Meat Intake and Markers of Adiposity and Inflammation: The Multiethnic Cohort Study.
9. Taskiran, et al (2023). The efficacy of systemic inflammatory response and oxidative stress in erectile dysfunction through multi-inflammatory index: a prospective cross-sectional analysis.
10. Nguyen, et al (2017). Vascular Endothelium.
11. Nikoobakht, et al (2005). The relationship between lipid profile and erectile dysfunction.
12. Moon, et al (2019). Obesity and Erectile Dysfunction: From Bench to Clinical Implication.
13. Iranmanesh, et al (2013). Glucose ingestion acutely lowers pulsatile LH and basal testosterone secretion in men.
14. Mulhall, et al (2018). Evaluation and Management of Testosterone Deficiency: AUA Guideline.
15. Kloner, et al (2016). Testosterone and Cardiovascular Disease.
16. Chu, et al (2001). Diabetes and Erectile Dysfunction.
17. Defeudis, et al (2022). Erectile dysfunction and diabetes: A melting pot of circumstances and treatments.
18. Pervin, et al (2021). Effect of alcohol on the central nervous system to develop neurological disorder: pathophysiological and lifestyle modulation can be potential therapeutic options for alcohol-induced neurotoxication.
19. Nunes (2023). Alcohol and the Etiology of Depression.
20. Liu, et al (2018). Erectile Dysfunction and Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
21. Dewitte, et al (2021). A Psychosocial Approach to Erectile Dysfunction: Position Statements from the European Society of Sexual Medicine (ESSM).
22. Pandit, et al (2023). Rare fatal effect of combined use of sildenafil and alcohol leading to Cerebrovascular Accident.