Collagen for Men: Why You Should Add This Protein to Your Stack
- By Rebekah Harding
- Fact-checked by Joy Ferguson
- July 11, 2023
T
here’s a reason longevity experts like Rhonda Patrick include collagen as part of their supplement stack and fitness-obsessed celebrities like Mark Wahlberg include it in their own brands: Recent studies suggest promising, healthspan-increasing benefits of collagen for men like building muscle, slowing skin aging, and boosting fat loss.
What is Collagen?
Think of collagen like the glue that holds your body together. Its primary job is to support the structure of your skin, bones, muscles, and connective tissues, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
This protein makes up around 30 percent of your body’s naturally produced protein. Around age 30, your body begins to produce less collagen and breaks it down faster. This can result in changes such as less skin elasticity and more fragile hair strands (1). By the time you’re in your sixties, you can be looking at deeper wrinkles and significant loss of muscle mass.
Types of Collagen
There isn’t just one collagen molecule that’s responsible for keeping your body in its best shape. Researchers have identified over 28 types of collagen in the human body. Here are five of the types responsible for helping your body maintain optimal function, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
Type I collagen
This version accounts for 90 percent of your body’s collagen and provides structure to your skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments (2).
Type II collagen
Type II collagen is found in elastic cartilage, where it is important for joint support (3).
Type III collagen
This form of collagen, found in organs, arteries and muscles, is a major structural component (4).
Types IV
Type IV collagen is found in some layers of your skin.
Types V
This form of collagen is found in the cornea of your eyes and some layers of the skin.
Who Should Supplement With Collagen?
While collagen can’t be measured in a blood test, your doctor may recommend that you supplement with collagen if you have certain autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. True collagen deficiency is quite rare, but is often associated with chronic stress, over-drinking, heavy smoking and extreme diets, says Kevin Huffman, M.D., a board-certified bariatric physician and founder of Ambari Nutrition.
“Signs of a collagen deficiency include early onset of wrinkles, early onset of joint pains, constantly fluctuating blood pressure or consistently high blood pressure, brittle nails and hair, organ prolapse and osteoporosis,” says Huffman.
Benefits of Collagen for Men
More muscle
Some time in your 30s or 40s, your muscle mass starts to decrease. Between 65 and 80, rates vary, but you may lose as much as eight percent each decade, according to the Cleveland Clinic. This natural age-related decline in muscle mass and strength is called sarcopenia. Between one and ten percent of your muscle mass is made up of collagen (5). Supplementing with collagen may help you boost your gains and stave off age-related strength loss.
In a study with 53 elderly male participants with sarcopenia, men who took 15-grams of collagen daily while on the same exercise regimen as the control group reported significantly higher muscle mass and strength gain (6). Researchers speculate that this increase may be due to the arginine and glycine amino acids in collagen, both known to support creatine synthesis, which, in some studies, was shown to improve muscle mass and function.
While many collagen supplements are marketed to women for hair and nail growth, celebrity fitness trainer and nutritionist Thomas DeLauer says that men may need more collagen than women to support muscle recovery. In a Youtube video, he points to a study that shows strength training in women converts to type 1A muscle fibers, while men tend to build more 2A muscle fibers (7). Type 1A fibers are more fatigue resistant but possess lower twitch speed, which means they provide less force. Type 2A fibers have a higher twitch speed, but are more susceptible to fatigue (8).
“Type 1A fibers don’t require as much protein, so women can get by with a little bit less,” DeLauer says. “Men need a bit more in the way of protein and collagen to support the type 2A muscle fibers.”
Greater fat loss
Research has suggested a link between collagen supplements and increased fat loss:
Participants who took a collagen supplement for 12-weeks showed a greater reduction in body fat percentage compared to the control group in a study published in 2019 (9). Researchers found that oral collagen supplements may have an anti-obesity effect even without increasing exercise or making participants go into calorie deficit.
Less hair loss
Many guys accept male pattern baldness as an inevitable part of the aging process. Makes sense, given around 85 percent of men will have significantly thinning hair by the time they’re 50 and about 25 percent of men who suffer with male pattern baldness will start to notice thinning before they reach 21, according to the American Hair Loss Association.
But some research suggests that replenishing your collagen may help slow your receding hairline (10). Oral collagen supplements may help prevent hair loss by decreasing TGF-β1 (a hair growth inhibitory factor) and increasing the expression of five other hair growth factors, according to an animal study published in 2022 (11).
Slower skin aging
Supplementing with topical or oral collagen may contribute to slowing skin aging and reducing wrinkles, according to a review published in 2022 (12). Researchers found that collagen had boosted skin moisture, elasticity, and hydration, and reduced the wrinkling and roughness of the skin associated with aging in the studies reviewed.
How to Increase Your Collagen
Eat collagen rich foods
Start with boosting intake of vitamin-C and vitamin-A rich foods, Johna Burdeos, a registered dietitian, says. Vitamin C and A are involved in collagen production (13).
Vitamin C rich foods:
- Citrus fruits
- Bell peppers
- Strawberries
- Broccoli
- Spinach
- Sweet potatoes
Vitamin A rich foods:
- Carrots
- Liver
- Dark green leafy veggies
- Red bell peppers
- Pumpkin
- Mango
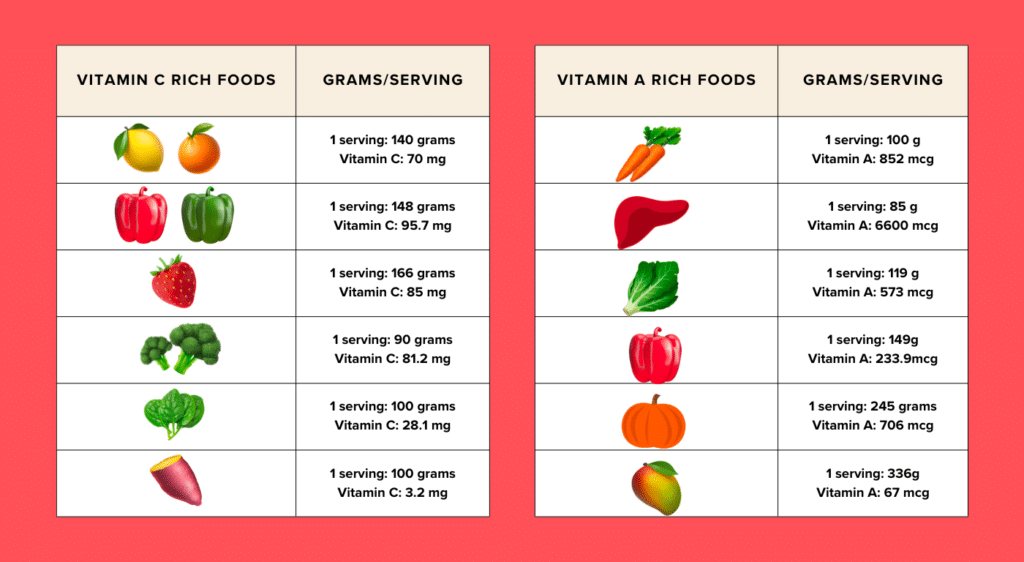
Some foods contain more of one type of collagen than others, which can help you support the specific system of your body that benefits from type I, II, III, IV or V collagens.
“It’s also important for men to consistently consume a balanced diet full of protein, minerals and vitamins, while getting enough sleep each day in order to boost collagen production and minimize its breakdown,” says Huffman.
Food High in Collagen
Cuts of meat that are full of connective tissue—think brisket, pot roast and chuck steak—are collagen-rich. Bone broth, the bones and skin of fish, and gelatin are also packed with collagen.
Foods to Boost Collagen Production
High protein foods that contain amino acids required for collagen production include eggs, legumes, soy, dairy, fish, poultry and meat. Since collagen production is also supported by nutrients like zinc, include zinc-rich foods like whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes and shellfish in your diet.
Collagen supplements
“When taking collagen supplements, aim for at most 20 grams of the collagen peptides each day, which equates to about two scoops of collagen peptide powders,” says Huffman.
Collagen supplements also frequently contain zinc and vitamin C that are linked to healthy hair and skin, and are required for collagen production. When selecting a supplement, look for one that contains multiple types of collagen.
References
1. Reilly, et al (2021). Skin collagen through the lifestages: importance for skin health and beauty.
2. Naomi, et al (2021). Current Insights into Collagen Type I.
3. Gencoglu, et al (2020). Undenatured Type II Collagen (UC-II) in Joint Health and Disease: A Review on the Current Knowledge of Companion Animals.
4. Kuivaniemi, et al (2019). Type III collagen (COL3A1): Gene and protein structure, tissue distribution, and associated diseases.
5. Gillies, et al (2011). Structure and Function of the Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix.
6. Zdzieblik, et al (2015). Collagen peptide supplementation in combination with resistance training improves body composition and increases muscle strength in elderly sarcopenic men: a randomised controlled trial.
7. Martel, et al (2006). Age and sex affect human muscle fibre adaptations to heavy-resistance strength training.
8. Potkin, et al (2021). Muscle Fiber Type Transitions with Exercise Training: Shifting Perspectives.
9. Tak, et al (2019). Effect of Oral Ingestion of Low-Molecular Collagen Peptides Derived from Skate (Raja Kenojei) Skin on Body Fat in Overweight Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.
10. Wang, et al (2011). Isolation and Characterization of Collagen and Antioxidant Collagen Peptides from Scales of Croceine Croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea).
11. Hwang, et al (2022). Hair-Growth-Promoting Effects of the Fish Collagen Peptide in Human Dermal Papilla Cells and C57BL/6 Mice Modulating Wnt/β-Catenin and BMP Signaling Pathways.
12. Al Atif (2022). Collagen Supplements for Aging and Wrinkles: A Paradigm Shift in the Fields of Dermatology and Cosmetics.
13. DePhillipo, et al (2018). Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review.














