How to Get Rid of Man Boobs (Moobs)
- By Gabrielle Kassel
- Fact-checked by Aviv Joshua
- January 26, 2024
So, your shirt isn’t sitting as smoothly against your sternum as you’d like. Or, you feel an uncomfortable jiggle when you jog. Maybe, your chest muscles are covered up by enlarged breasts that are tender to the touch (1). In that case, you’re probably a card-carrying member of the Man Boob Club, alongside studs like Simon Cowell, Jack Nichols, and Ben Affleck. And if you’re wondering about how to get rid of man boobs, know that you’re not alone.
Given that moob-owners are raking in fat stats and shacking up with timeless babes like J-Lo, it should be clear that man moobs are nothing to fret about, from an aesthetic point of view. But, for many of the one-third of guys worldwide who have them, man boobs are a source of shame—and confusion (2). After all, given how hush-hush the topic is, most guys don’t understand what’s causing their moobs, or if getting rid of them is even possible.
There may be some health risks associated with having a little extra on top, too. A recent Danish study of more than 20,000 men found that having man boobs may increase the risk of premature death by as much as 37 percent (3). But it’s not the breast tissue itself that’s to blame—moobs may be indicative of a larger health issue at play.
Ahead, health professionals answer all of your questions about what man boobs are, how they develop, and how to get rid of them—because yes, it’s possible.
What Are Man Boobs, Exactly?
Man boobs and moobs may be the preferred locker room slang, but there’s a clinical term for them: Gynecomastia.
“Gynecomastia is the medical term for the presence of over-developed breast tissue or excessive fat in the chest region in people assigned male at birth,” says plastic and reconstructive surgeon Ashley Steinberg M.D. F.A.C.S., who specializes in gynecomastia. There are two main types of gynecomastia, glandular proliferation gynecomastia and pseudogynecomastia, which have different underlying causes, and therefore treatments, she says (2).
Glandular proliferation gynecomastia: Also known as ‘true gynecomastia’ or simply ‘gynecomastia’, glandular proliferation gynecomastia is a true medical condition marked by an excess in glandular breast tissue under the nipple and areola, she explains.
Pseudogynecomastia: Steinberg explains pseudogynecomastia describes excess fatty, breast tissue surrounding the chest. These ‘man boobs’ may develop after packing on some extra pounds, she says.
Both types of moobs can make your chest look swollen, puffy, and bulbous. But, while they look the same to an untrained eye, a medical professional will be able to determine which you have from a physical exam.
“True gynecomastia creates tissue that’s very firm to touch, and the roundness is typically relegated to the area just under the nipple and areola,” Steinberg says. Constance M. Chen M.D., board-certified plastic surgeon and breast reconstruction specialist, agrees, adding that this type of gynecomastia feels very similar to the defined breasts you’d expect to feel on a person assigned female at birth.
Pseudogynecomastia breasts are soft and squishy to touch, Steinberg explains. Plus, fat tends to be more equally distributed throughout the chest region, while breast gland tissue tends to create a cone-like appearance, she says.
Ashley Steinberg M.D. F.A.C.S. is Houston, Texas based plastic and reconstructive surgeon who specializes in gynecomastia.
Constance M. Chen M.D., board-certified plastic surgeon and breast reconstruction specialist.
Jake Harcoff C.S.C.S. is certified strength and conditioning coach and the head coach and owner of AIM Athletic, a training hub designed to safely, and efficiently achieve a pain-free, strong body that lives a healthy body-fat percentage.
Carly S. is a fat activist, pleasure expert, and sex educator who helps people of all sizes, genders, and sexualities embrace their bodies for more pleasurable lives. She is also the founder of Dildo or Dildon’t, an online pleasure product review platform.
What Causes Man Boobs?
Given how rarely it is talked about, you’ll probably be surprised to learn that 50-65 percent of guys deal with moobs at some point of their lives (4). Though, given the fact that gaining body fat can cause moobs, some health experts predict they will become more prevalent—especially as obesity rates continue to rise (5).
Ahead, check out the three most common causes of man boobs.
1. Hormone imbalance
The main culprit behind true gynecomastia is hormone imbalance—or more specifically, excess estrogen. “When there are excess estrogens relative to the amount of androgens circulating in the body, it can induce gynecomastia,” Steinberg says (6). Testosterone is a type of androgen in the body, she explains (7). So, if T-levels dip for whatever reason—and there are many possible causes—that may increase the risk for moobs, she notes.
For example, testosterone levels can dip in response to thyroid dysfunction, chronic disease (such as type 2 diabetes), testicle injury, medication or treatment side effects, or an underlying infection (including coronavirus and tuberculosis (8).
Meanwhile, estrogen levels can rise in direct response to lower testosterone (7). Estrogen levels can also be high if you have any chronic conditions such as diabetes or hyperthyroidism, Steinberg says.
In men, hormone imbalance is typically associated with symptoms like fatigue, erectile dysfunction, inability to put on muscle, and brain fog (9). If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms— in addition to having chest chub—consider booking an appointment with an endocrinologist or relevant clinician (or consider ordering an at-home hormone test from Hone).
2. Obesity
Weight gain can elevate your risk for both pseudogynecomastia and true gynecomastia, Steinberg says.
“When you put on fat all over [your body], you can put on fat in your chest area,” she explains. The result, as you might guess, can be pseudogynecomastia. But the association between obesity and true gynecomastia goes beyond that.
Fatty tissue produces a hormone called leptin so when body fat goes up, so does leptin production (10).
When produced in proper quantities, leptin functions as an appetite modulator, letting your body know when you have eaten enough. When too much leptin is produced, as is the case with those who have obesity, the brain stops responding to this all-important signal (11). This can cause you to keep eating well after you’re physiologically full.
Further, the entire endocrine (hormone) system is interconnected. As leptin levels rise, it impacts the levels of other hormones in the body. Research found in Androgens: Clinical Research and Therapeutics suggests leptin and testosterone are inversely related, meaning as leptin levels rise, testosterone levels drop (12). “This causes an imbalance between estrogen and testosterone to occur,” Steinberg explains, adding that estrogen levels will begin to increase as a result.
Generally, any healthy—and physician-approved—obesity intervention that targets fat loss will reduce the size of moobs. However, it’s important to note that any granular breast tissue that has grown as a result of true gynecomastia may not go away through just diet changes. That’s when either increased body acceptance or surgery are required, but more on that below.
3. Medication
The list of medications that can cause gynecomastia is long. Antibiotics, opioids, HIV medications, anti-ulcer drugs, and chemo drugs have all been reported to induce breast tissue growth (13, 14). Hair loss drugs, anabolic steroids, and diuretics are also associated with the development of man boobs (15, 16).
The relationship between a drug and gynecomastia is not always clear, Steinberg notes. Most commonly, however, the side effect stems from the way the drug interferes with hormone production or reception, she says.
To be clear: It isn’t just prescription drugs that can have this unwanted side effect. “Marijuana is a common cause of gynecomastia, as it works on estrogen receptors in the body,” Steinberg says. Indeed, a study published in a 2022 issue of Frontiers In Reproductive Health suggests there may be a link between smoking weed and endocrine system dysregulation (17).
Whether you blame your moobs on prescription or recreational drugs, your first move is to chat to a healthcare provider. They can prescribe another medication that counteracts the hormone imbalance or prescribe a new medication entirely that does not have gynecomastia as a side effect. They can also help you come up with a game-plan to quit any recreational drugs safely.
How to Get Rid of Man Boobs
Whether your man boobs are caused by body fat, granular breast tissue growth, or a combo, there are interventions you can take to reduce their appearance.
1. Talk to your physician about breast reduction options
The only way to get rid of granular tissue growth associated with true gynecomastia is surgery, according to Steinberg.
“Regardless of whether it’s caused by something you can’t control like puberty or something you have more control over like steroid use, once the breast tissue grows, it isn’t going to go away on its own,” she explains. It can, however, be surgically removed with an outpatient procedure called excision, which involves making an incision in the skin, then cutting out the breast tissue, she explains.
Sometimes surgery is also performed on individuals with pseudogynecomastia. “If there is not a lot of excess skin, then liposuction may be used to remove the fat,” Chen says. “If the breasts are large or droopy, then liposuction will be used alongside skin removal to tighten the breast envelope and create a more desirable shape,” she says.
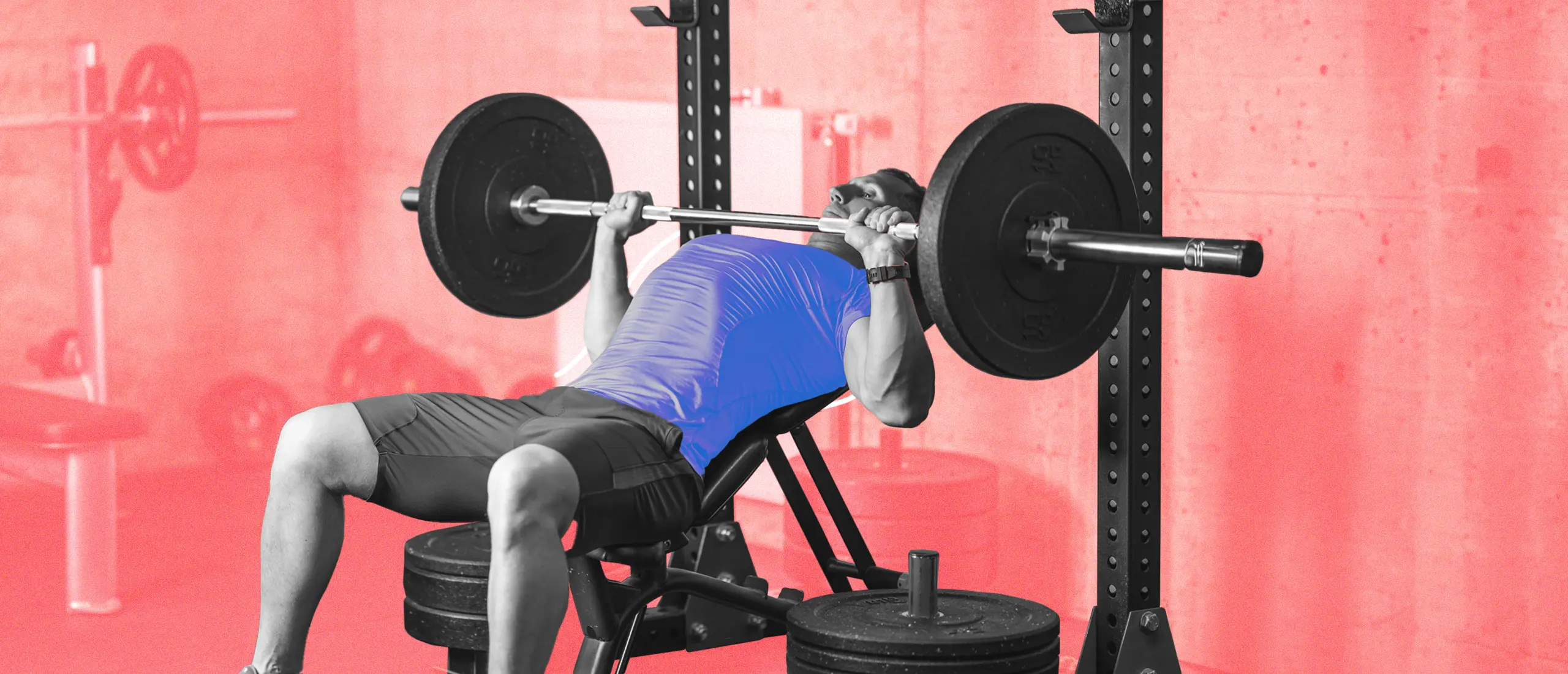
2. Lift heavy weights
You cannot lift away excess breast tissue, but you can replace excess fat with muscle when you follow a solid strength training routine.
“The body tends to lose fat systematically rather than from targeted regions,” says certified strength and conditioning coach Jake Harcoff, C.S.C.S. That means that while you can’t lose fat just from your chest, losing overall body fat will have a trickle-down effect on the chest region.
“It is crucial that those with excess chest fat adopt a comprehensive approach rather than fixating on isolated training,” he says. Rather than just focusing on push-ups and bench pressing, for instance, he suggests adopting a full-body strength training plan with compound exercises like back squats, deadlifts, cleans, and shoulder presses.
“The optimal rep range for fat loss generally falls in the moderate range of around 12 to 15 reps per set,” he says. Choose a weight you can crank out that amount of reps with and perform until failure. “Leaving just 1 to 2 reps in the tank has been shown to be most effective for muscle growth regardless of the total reps completed,” he explains (18).
3. Perform exercises that specifically target your chest
Isolated chest exercises won’t necessarily help you lose chest fat, but they will help sculpt the muscles underneath, Harcoff says. “Consistently training the chest two times per week will help to build up the upper body muscles, which can help people achieve the particular chest contour they are after,” he says.
Bench pressing variations recruit multiple muscle groups, including the chest, shoulders, and triceps, “making it efficient for overall upper body strength and muscle growth,” Harcoff adds. What sets weighted movements, such as the bench press, apart from body weight exercises, is ease of tracking and progressing with weight, he says. Barbells and dumbbells make it easy to up the resistance, which means you can keep making the movement harder as your muscles get stronger.
“To maximize the effectiveness of benching it’s crucial to maintain proper form,” Harcoff notes. “Take care to grip the weights in such a way that both arms make approximately a 45-degree angle from the body.” This will help target and stimulate muscle growth in the pectoral muscles.
4. Fine tune your diet
Overall fat loss is key for shedding moobs, and adopting a balanced diet is a powerful way to decrease body fat (19). Consider working with a registered dietitian to develop a macronutrient intake plan aligned with your needs and fitness (or aesthetic) goals.
Chen recommends prioritizing nutrient dense foods. “If you have gynecomastia, it’s best to stick to a healthy diet of fruits and vegetables, lean meats and fish, healthy fats, and whole grains,” she says. These nutrients will help give your body the tools it needs to build muscle following your workout, notes Harcoff, as well as help keep insulin levels steady to keep you from overeating (20).
In the interim, fill your social media feeds with diverse body shapes
“Media typically makes fat people the unsexy friend or the butt of jokes,” says fat activist and pleasure expert Carly S., founder of Dildo or Dildon’t. But neither sexiness or comedic prowess are relegated to one particular body type. Seeing non-traditional and fat bodies on your social feeds can be a really empowering way to remember that, she says. Over time, this can help you replace a desire to get rid of moobs with an increased acceptance of them.
In a similar spirit, consider talking about moobs with your pals or partner(s)—they can help you feel good about yourself as you are right now, she notes. “You never know what someone is dealing with or insecure about and they might be able to understand and relate to your insecurities,” she says. “And if that isn’t the case, take a step back and really examine your relationship with that person.”
The Bottom Line
Whether caused by body fat, tissue growth, or a combination, man boobs are common, normal, and don’t have to be permanent if you don’t want them to be. Because the sudden appearance of moobs can be caused by hormone imbalances, obesity, and side effects to certain medications, make sure to consult with your healthcare provider about an action plan.
No matter the root cause of your moobs, there are lifestyle or surgical interventions you take to get rid of them.
References
1. United Kingdom National Health Service (NHS). What is gynaecomastia?
2.Neslihan Cuhaci, et al. (2014). Gynecomastia: Clinical evaluation and management.
3. Elvira V Bräuner, et al. (2024). Is male gynaecomastia associated with an increased risk of death? A nationwide register-based cohort study.
4. Cleveland Clinic. Enlarged Male Breast Tissue (Gynecomastia).
5. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Overweight & Obesity Statistics.
6. Ronald S. Swerdloff, et al. (2023). Gynecomastia: Etiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment.
7. David J Handelsman, et al. (2020). Androgen Physiology, Pharmacology, Use and Misuse.
8. MedlinePlus. Could you have low testosterone?
9. Mount Sinai. Male Hormone Disorders.
10. Catalina Picó, et al. (2022). Leptin as a key regulator of the adipose organ.
11. Sean Dornbush; et al. (2023). Physiology, Leptin.
12. Thiago Fernandes Negris Lima, et al. (2020). Association of Leptin with Total and Free Testosterone: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys.
13. Fnu Deepinder, et al. (2012). Drug-induced gynecomastia: an evidence-based review.
14. Mayo Clinic. Enlarged breast tissue in men (gynecomastia)
15. Yuval Ramot, et al. (2009). Finasteride induced Gynecomastia: Case report and Review of the Literature.
16. Umme Aiman, et al. (2009). Gynecomastia: An ADR due to drug interaction.
17. Thiago A. Teixeira, et al. (2022). Marijuana Is Associated With a Hormonal Imbalance Among Several Habits Related to Male Infertility: A Retrospective Study.
18. Sanmy R. Nóbrega, et al. (2016). Is Resistance Training to Muscular Failure Necessary?
19. Darryn Willoughby, et al. (2018). Body Composition Changes in Weight Loss: Strategies and Supplementation for Maintaining Lean Body Mass, a Brief Review.
20. Fátima O. Martins, et al. (2022). Impact of Diet Composition on Insulin Resistance.