A Dietitian Settles the Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke Debate Once and For All
- By Rebekah Harding
- April 18, 2024
Our product picks are editor-tested, expert-approved. We may earn a commission through links on our site.
T
here are many reasons people have ditched regular Coca-Cola. For one, a single can of Coke packs 140 calories and 39 grams of sugar (1). The American version of the cult-classic soda also contains high fructose corn syrup, which may increase appetite and damage your liver more than table sugar (sucrose) (2). But when it comes to picking out a Coke alternative, many soda lovers may struggle to pick a side in one fierce competition: Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke.
We’re not saying diet soda is healthy for you, at least, not compared to these healthier soda alternatives. But If you’re trying to pick between one of the zero sugar, no-calorie options (or want to make your favorite whiskey and Coke a little less bad for you), you’re probably wondering which is healthier: Coke Zero or Diet Coke?
To settle the debate once and for all, we tapped a registered dietitian for the details on each beverage’s nutrition label.
Our Experience
Hone Health is a team of health-obsessed journalists, editors, fitness junkies, medical reviewers, and product testers. To ensure we deliver you research-backed information on energy drinks, we’ve spoken to a registered dietitian nutritionist and reviewed several research studies and well-respected medical pages.
About the Expert:
Lena Bakovic, M.S., R.D.N., C.N.S.C., is a registered dietitian with Top Nutrition Coaching. She specializes in chronic disease, weight management, and gut health.
Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke: Ingredients

Coke Zero
Below are all 10 of the ingredients you can find in a can of Coke Zero (3):
- Carbonated water
- Caramel color
- Phosphoric acid
- Aspartame
- Potassium benzoate (to protect taste)
- Natural flavors
- Potassium citrate
- Acesulfame potassium
- Caffeine
- Phenylalanine
Diet Coke
Catch these 9 ingredients on the back of your Diet Coke (4):
- Carbonated water
- Caramel color
- Aspartame
- Phosphoric acid
- Potassium benzoate (to protect taste)
- Natural flavors
- Citric acid
- Caffeine
- Phenylalanine
Coke Zero and Diet Coke have near identical ingredients. Coke Zero includes two types of artificial sweeteners—aspartame and acesulfame potassium—whereas Diet Coke is only sweetened with aspartame. Why should you care? Both artificial sweeteners are controversial—here’s the scoop:
Aspartame: Both beverages contain aspartame, a zero-calorie sweetener made from phenylalanine and aspartic acid (5).
While aspartame is currently FDA approved, researchers believe that it may be linked to mood changes, toxic liver disease, and may also have carcinogenic effects (6). However, further human clinical trials are needed.
Acesulfame potassium: On top of aspartame, Coke Zero also contains acesulfame potassium, which is another zero-calorie sweetener.
Like most artificial sweeteners, acesulfame potassium is controversial as some studies suggest consuming it over time may be linked to an increased risk of cancer (7). Still, the National Cancer Institute, the World Health Organization (WHO), and FDA all agree that the sweetener is safe for human consumption at amounts of 50 mg per kilogram (kg) (1 kg=2.2 pounds) of body weight per day (8).
Ingredients Winner: Coke Zero
While the two formulas share most of the same ingredients, artificial sweeteners like Aspartame are higher on the list for Diet Coke. (For context, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires that ingredients are listed in order of their prominence and weight.)
Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke: Nutrition
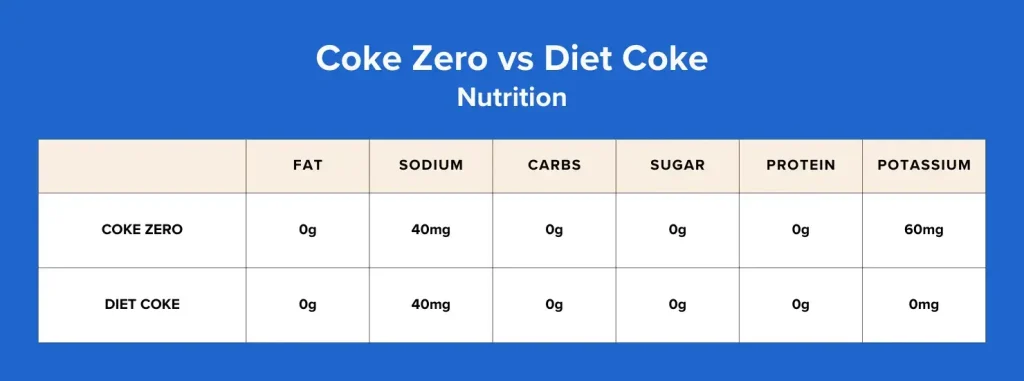
Here are the nutrition facts of a 12 fluid ounce (fl oz) can of Coke Zero:
- 0 g total fat
- 40 milligrams (mg) sodium
- 0 grams (g) carbohydrates
- 0 g total sugars
- 0 g protein
- 60 mg potassium
And the nutrition facts for a 12 oz Diet Coke:
- 0 g total fat
- 40 mg sodium
- 0 g carbohydrates
- 0 g total sugars
- 0 g protein
Sweeteners
Both Coke Zero and Diet Coke are made with artificial sweeteners that are 200 to 700 times sweeter than table sugar (9).
Diet Coke is sweetened with aspartame, whereas Coke Zero contains both acesulfame potassium and aspartame. Registered dietitian Lena Bakovic, R.D.N. says both drinks have a neutral effect on your blood sugar levels, meaning they won’t cause your levels to spike after drinking them (unlike a can of regular Coke).
However, Diet Coke isn’t remarkably healthier because it only contains one artificial sweetener, Bakovic suggests.
She also mentions that some people may want to avoid artificial sweeteners if they are sensitive to them or are nervous about their potential carcinogenic (cancer-causing) effects (7, 6). If you’re sensitive to artificial sweeteners, you may experience digestive discomfort (like bloating and gas) or headaches after consuming them (10, 11).
Calories
There are zero calories in both Diet Coke and Coke Zero. (Yup, that also means these diet sodas won’t break your fast.)
Sodium
Both sodas have an equivalent amount of sodium, with each containing 40 mg in a one can (12 fl oz) serving.
“This is about 2 percent of the daily value for sodium for the entire day, which is technically considered low in sodium,” Bakovic says.
Caffeine
Diet Coke contains 12 mg more caffeine than Coke Zero, with 46 mg and 34 mg, respectively.
People who are more sensitive to caffeine—or who want a little less buzz after enjoying a few cups of coffee before lunch—may want to choose Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke, Bakovic suggests. Keep in mind that one cup of coffee has around 95 mg of caffeine in it—so an extra 12 mg will likely not make much of a difference.
Plus, both options also come in caffeine-free versions.
Nutrition Winner: Tie
The nutritional value of both beverages is very similar, says Bakovic. But if you’re looking for a tie breaker, one key difference between the two is the caffeine content. If you’re sensitive to caffeine, Diet Coke does have a slightly higher caffeine content than Coke Zero. But you can cut the caffeine out altogether by opting for the caffeine-free versions of both products.
Coke Zero vs. Diet Coke: Taste
We know what you really care about. Between Coke Zero and Diet Coke, which soda actually tastes better? We tried both to give you an honest review.
Diet Coke has an almost bitter, but not unpleasant, aftertaste. It’s completely different from its sugar-laden counterpart, Coca-Cola. However, if you prefer a more mild-tasting version of the fizzy drink, you’ll probably love Diet Coke.
On the other hand, Coke Zero tastes very similar to the original formula and is way sweeter than Diet Coke—almost syrupy to taste. We find it hard to believe there’s no real sugar in it.
Taste Winner: Coke Zero
While Diet Coke and Coke Zero are both beloved by soda drinkers, Redditors also agree that Coke Zero tastes more similar to the original Coca-Cola. Some might see this as a bonus.
References
1. SmartLabel. Coca-Cola Nutrition Facts.
2. Mai, et al (2019). The negative and detrimental effects of high fructose on the liver, with special reference to metabolic disorders.
3. Coca-Cola. Coca‑Cola® Zero Sugar.
4. Coca-Cola. Diet Coke®.
5. European Food Safety Authority. Scientific Opinion on Aspartame.
6. Czarnecka, et al (2021). Aspartame—True or False? Narrative Review of Safety Analysis of General Use in Products.
7. Debras, et al (2022). Artificial sweeteners and cancer risk: Results from the NutriNet-Santé population-based cohort study.
8. Science Direct. Acesulfame Potassium.
9. Johns Hopkins. Facts About Sugar and Sugar Substitutes.
10. Spencer, et al (2016). Artificial Sweeteners: A Systematic Review and Primer for Gastroenterologists.
11. Newman, et al (1989). Aspartame as a dietary trigger of headache.











